Your website is like a digital office space for your business. Everything about it shows users the kind of brand you are and if you can be trusted or not. One of the best ways to communicate trust from the start is with an SSL certificate.
An SSL certificate secures your website by encrypting the back-and-forth information between the user’s browser and the web server. It protects private customer data from hackers by preventing them from intercepting information when users browse the website.
In most cases (roughly 99%, if not 100%), your hosting provider will give you a free SSL certificate as part of your web hosting package. So, even if you subscribe to the cheapest shared hosting plan available, you’ll often get an SSL certificate. However, usually, you get what you pay for – sometimes, it makes sense to purchase another, more advanced protection.
In this guide, we will explore the different types of SSL certificates, how to install them on your website, and the best way to manage them for optimal website protection. Stick around!

Source: https://pixabay.com/vectors/laptop-ssl-icon-secure-green-lock-7336401/
What Is an SSL Certificate?
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital document that authenticates the identity of a website while allowing for encrypted connections and greater security. It helps you verify the identity of the origin server, which means cyber criminals cannot spoof domains, carry out on-path attacks or impersonate authenticated websites.
An SSL certificate is compulsory for websites that use HTTPS encryption. HTTPS creates an encrypted connection between a web server and a user’s browser, preventing information from being intercepted and corrupted.
The SSL certificate contains various details, including the website’s domain name, the certificate authority, the validity period of the certificate, the public key, and the CA’s digital signature.
While an SSL certificate isn’t technically compulsory for all websites, websites that process sensitive data such as credit card information, personal details, or login credentials should absolutely use HTTPS to ensure secure data transmission. Furthermore, search engines like Google prioritize HTTPS websites in their search results, which can have significant SEO benefits.
Simply put, having an SSL certificate has become the norm for online business success. Yet, you need to choose the right one for your needs.
The Different Types of SSL Certificates
Each type of SSL certificate has its own benefits and is suited to different situations depending on the structure and needs of your website or business.
Based on the level of authentication and verification provided by the Certificate Authority (CA), you can choose from Domain Validated (DV), Organization Validated (OV), and Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificates.
Moreover, at AltusHost, we enable you to choose an SSL certificate based on the number and type of domains or subdomains you want to secure.
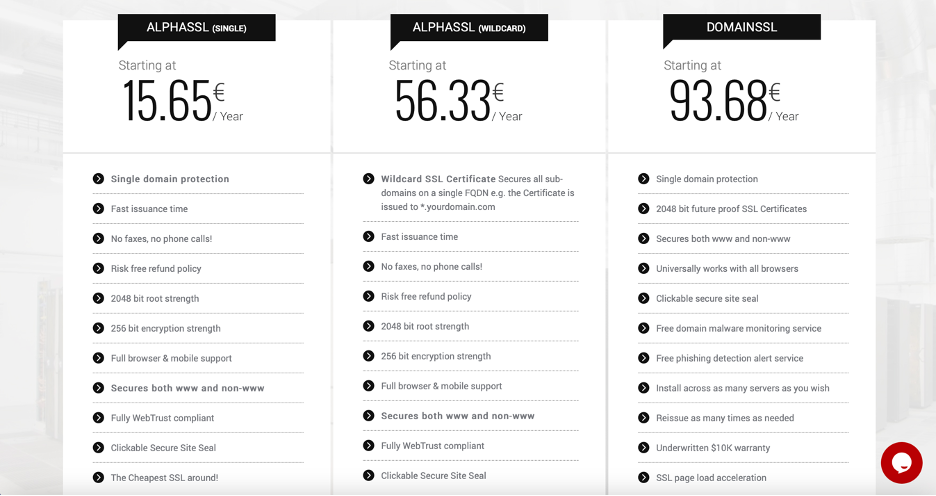
Source: https://www.altushost.com/ssl-certificates/
Single Domain SSL Certificate
A single-domain SSL certificate is limited to only one domain name. Therefore, you cannot use this type of certificate to verify any other domain, including the subdomains of the initial DNS. However, it will automatically authenticate all the pages on this domain.
For example, if the single domain SSL certificate authenticates altushost.com, then the same certificate will also authenticate its subpage altushost.com/ssl-certificates/.
Wildcard SSL Certificate
The Wildcard SSL certificate has a broader reach than the single-domain SSL certificate. This certificate authenticates a single domain along with all its subdomains. The most popular subdomain for most websites is www. However, some websites use multiple subdomains to help users navigate the website faster and better.
For example, if a Wildcard certificate authenticates a DNS like www.example.com, it will also authenticate subdomains under it, such as blog.example.com, support.example.com, contact.example.com, and so on.
Multi-Domain SSL Certificate
Multi-domain SSL certificates protect multiple domains at once. Domains and subdomains can share a single multi-domain SSL certificate. For example, a single SSL certificate can validate example.com, notsosure.com, and any other independent DNS.
The Average Cost of SSL Certificates
Single-domain SSL certificates are the cheapest SSL certificates available. On the other hand, multi-domain wildcard SSL certificates are the most expensive because they have the most utility.
Here’s a breakdown of the cost of SSL certificates at AltusHost.
| SSL Certificate Type | Price / Year |
| AlphaSSL (Single) | 15.65 € / Year |
| AlphaSSL (Wildcard) | 56.33 € / Year |
| DomainSSL | 93.68 € / Year |
Investing in an SSL certificate makes sense as it ensures website security, fosters user trust, and enhances credibility. It also boosts SEO rankings, as search engines prioritize HTTPS-enabled websites. These factors increase your website visibility and, consequently, business performance.

Source: https://pixabay.com/illustrations/data-key-key-shut-down-to-graduate-571156/
How to Install an SSL Certificate?
Most managed hosting providers offer free SSL certificates, automatically installing them on your website. However, if you want to install an SSL certificate manually, follow these steps.
Step 1 – Purchase an SSL certificate from AltusHost
Once you’ve chosen the correct type of SSL certificate based on your needs and budget, you can purchase it from a trusted certificate authority like AltusHost.
Source: https://cp.altushost.com/?/cart/ssl-certificates/
You can also decide to obtain the certificate from GoDaddy, Namecheap, or any other platform you choose.
Step 2 – Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
After you have purchased the certificate, you need to generate a certificate signing request on a web server. You can still use the hosting provider you bought the certificate from initially.
For example, if you buy your SSL certificate on AltusHost, you can generate a CSR immediately.
Step 3 – Get Your Approved SSL Certificate
The next step is to submit the CSR and other details to the hosting provider. They will then process your request and issue you a valid SSL certificate once it is ready.
This new certificate will include the initial SSL certificate, necessary files, a root certificate, and intermediate certificates.
Step 4 – Log in To Your Control Panel
Next, you head toward your control panel on the hosting platform and locate your SSL/TSL settings. If it is a cPanel, you can easily find the section for these settings.
Step 5 – Input the SSL Files
After locating the SSL settings, look for the option to install/upload your SSL certificate. For this purpose, you will need a private key, the intermediate certificates, and the SSL certificate itself.
AltusHost (and other hosting providers) will often provide documentation on how to go about this process.
Step 6 – Make Sure Your Website Is SSL Configured
Once you have successfully uploaded those documents and installed your SSL certificate, you need to configure your website. This configuration will ensure your website can use HTTPS and is loaded securely. You may need to update your website’s settings to complete the HTTPS connections.
Step 7 – Test the Certificate on Your Browser
Once all this is done, run the website on your browser to see if it worked. You should see a padlock sign at the top left corner of your search bar followed by an https:// before the DNS of your website.

Source: https://pixabay.com/illustrations/https-website-internet-security-3344700/
Tips for Managing Your SSL Certificate
SSL certificates have expiry dates, and they are also susceptible to attacks like every other part of the internet. Therefore, you need to manage them well if you want the best website security.
Here are some of the best tips for managing your SSL certificate.
Choose A Reliable Certificate Authority
Most hosting providers are SSL certificate authorities. However, not all of them are reliable. You need to consider their customer support, pricing (some are way more expensive than others), and reputation. Additionally, consider their certificate management tools, ease of certificate renewal process, and the range of certificate types they offer.
For instance, you can use AltusHost, GoDaddy, or Namecheap as three reputable market choices.
Get the Right Type of Certificate
Depending on your needs, you may require a single domain, wildcard, or multi-domain SSL certificate. Evaluate your requirements carefully to ensure you get the appropriate type of certificate without overspending on unnecessary features.
Regularly Monitor and Renew Certificates
SSL certificates are not a one-time purchase. They do have expiration dates, and you need to keep renewing them. Keep track of your SSL’s expiration date and renew it before the time elapses.
Fortunately, many certificate authorities have tools that automate the renewal process. They are free, and all you need to set up your payment channel.
Remember, if your SSL goes off even for a day, you might lose a considerable amount of traffic and revenue from your website.
Update Your SSL Software Regularly
Encryption standards evolve rapidly. So, updating your SSL configurations and software regularly to ensure you’re using the most secure protocols is the icing on the cake.
Outdated software comes are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and malware. So make sure to keep your plugins, software, and SSL configurations up to date.

Adhere to Best Practices for Key Management
Last but not least, always protect your private keys. Store them securely and consider using hardware security modules for high-security environments. Regularly update and change keys to mitigate risks.
Final Thoughts
Your SSL certificate is an integral part of your website and a huge piece of your overall online brand image. If your audience finds your website and Google labels it as “Not secure,” you will likely lose that traffic forever.
Before you launch your website, make sure your SSL certificate is in order. We’ve already shown you the basics; now, it’s time to get to work!



